Among the many diseases of the joints, osteoarthritis is more common.With the development of this pathology, the patient begins to have problems with limb mobility, swelling, inflammation and intense pain syndrome occur.And if we talk about the causes of knee joint arthrosis at a young age, then they can include many predisposing factors.
General information
The development of deformation processes in the field of knee joint in official medicine is called gonartrosis.The disease is associated with degenerative-district phenomena in the hyaline cartilage, which develop in stages and offer many problems for the patient.The main signs of the disease include:
- Pain syndrome.
- Movement station.
- Inflammation.
- Edema
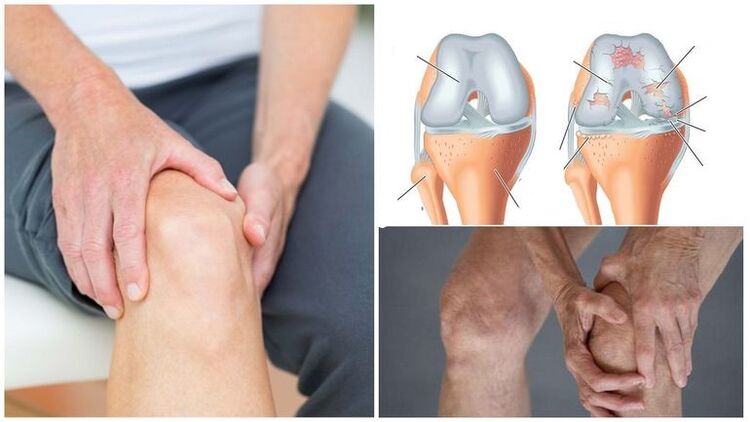
Among the different forms of arthritis, damage to the knee joint is considered the most common.In most cases, the problem progresses in women aged 40 years.It can also appear in young people against the backdrop of mechanical damage or colossal stress.For example, professional athletes are the most affected by this pathology.
If you do not take appropriate measures in the early stages of the development of the disease, then over time, the gonarthrosis will become a severe form, which will have irreversible consequences.The dimensions of the joint will begin to grow at a tremendous speed, the deformation process will begin in the cartilage and bones, and any physical activity will be associated with severe pain and discomfort.At worst, the patient will completely lose the opportunity to move independently.
Many mistakenly think that arthritis and arthritis are the same pathologies.However, the first disease implies an acute inflammatory reaction, and the second - a number of chronic diseases with a degenerative character.If the patient has the symptoms of both problems, he can be diagnosed with arthroso-arthritis.
Causes of knee joint arthrosis
The causes of the disease are very different, so it is problematic to distinguish one.In most cases, the development of the problem appears with the emergence of some provocative factors that cause violations.Modern medicine identifies such arthritis mechanisms:
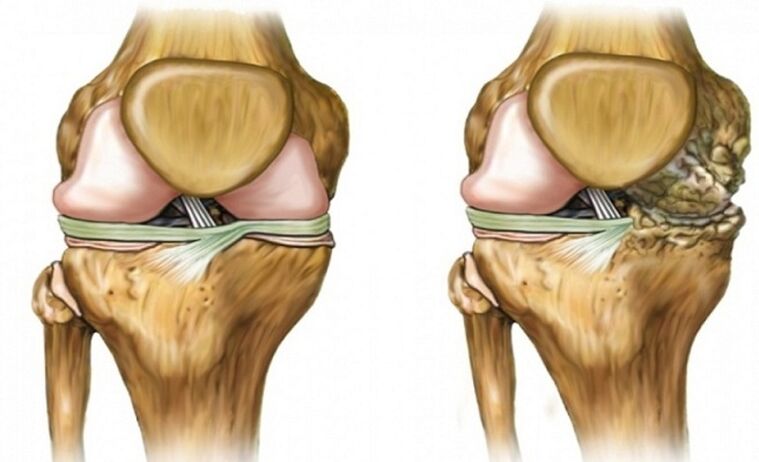
- Primary is a natural process that occurs in people aged 40, and is explained by aging body tissue.The main mechanism for arthrosis development also contributes to associated factors, including overweight, inheritance or high loads.
- Secondary - covers 30% of all disease arthrosis.The cause of the occurrence is associated with the transfer of mechanical damage, lower leg fractures or ligament fractures.The first symptoms of pathology can occur several years after injury.However, with serious injuries, this can occur after 2-3 months.
There is another development mechanism, which owns 7-8% of arthrosis cases.As follows: If a person aged 40 started running or professional sports, this can lead to rapid dystrophic and degenerative changes.Moreover, arthritis also manifests itself in concomitant diseases, including various forms of arthritis, gout, overweight, etc.
The reasons for developing the disease are often associated with intense loads, weight lifting or frequent steps (especially in old age).Patients who have suffered spinal injuries or neurological diseases also fall into the risk area.
In most cases, the predisposing factor in the appearance of gonarthrosis is muscle spasms on the front surface of the thigh.Since the appearance of first pain, the pathology may not manifest for a long time, and the only signs will be characteristic fatigue and severity in the legs.
Stages of development and symptoms
Once you have realized that from the appearance of knee joint arthrosis, you can begin to study the main symptoms and stages of the development of the disease.Experts argue that pathology is characterized by slow progress as negative symptoms increase.Depending on the patient's ability to work, three stages of arthrosis are distinguished:
- At first
- The second.
- Third.
It should be noted that gonarthrosis does not have an acute form of course, because it is a degenerative process of a chronic nature.As for the term "acute arthrosis", in most cases it has to do with the third stage with weighted symptoms.
First stage
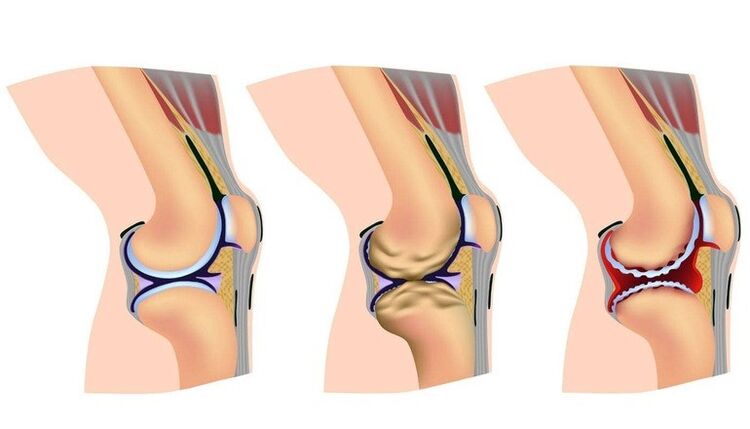
In the first phase of gonartrosis in the joint, the circulation of a particular fluid begins to worry, which nourishes it and lubricates.Special changes in the structure are not observed, and the cartilage fabric is slightly inflamed.
The initial stage of arthrosis development is associated with little discomfort and a sense of stiffness during movement.The patient becomes problematic to climb the steps, make remote races or stand up for a long time.Anydo increased activity leads to the appearance of knee pain.However, in the slightest rest, the pain syndrome is localized and disappeared.
Further progression of pathology increases the pain, but the patient's ability to work does not worry in any way.In this regard, the patient continues to lead the usual lifestyle.
It is not easy to determine the development of arthrosis in the early stages.The fact is that people simply cannot notice the symptoms, attributing everything to excessive work.
The second and third degree
Between the initial symptoms and the passage of pathology in the second phase can last several months.At the same time, the patient may forget the first symptoms for some time and continue to live an ordinary life.But the advancement of degenerative changes will have more serious consequences, namely:
- Enlarged pain in any load.
- Movement station.
- Edema
- Inflammation.
In addition to the symptoms described, a crisis in the knee joints will also appear, which is explained by a violation of the structure.The cartilage tissue will begin to become thinner, and the volume of synovial fluid, which lubricates and nourishes the joint, will decrease significantly.
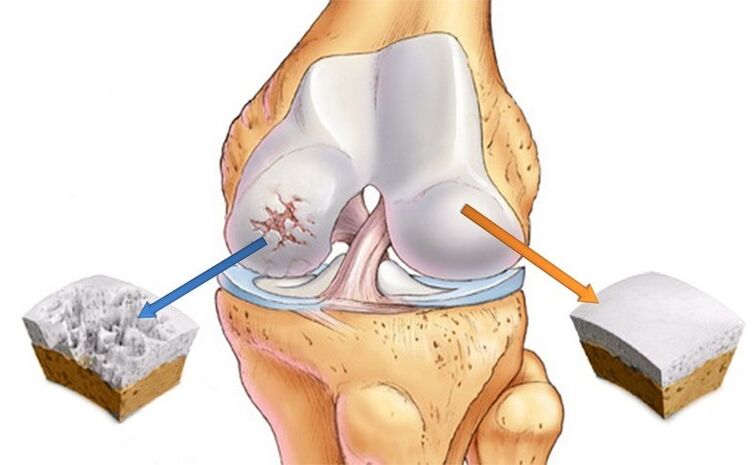
If the patient does not start treatment in the second stage of arthrosis, this will lead to the development of the third, more dangerous.It is a very neglected form of the pathology, in which the union loses its basic functionality, and the patient's ability to work is at risk.
In this case, the content of synovial fluid in the cartilage tissue becomes minimal, the cartilage loses its previous thickness, and the bones thicken.In the affected area, a lymphatic fluid also appears and an inflammatory process is initiated.
In an advanced form, gonarthrosis has such symptoms:
- Too severe pain syndrome, which occurs in every movement.Moreover, even if the patient is in a stretched or sitting position without activity, he can suddenly feel severe pain.
- Knee joint motor skills are very limited.
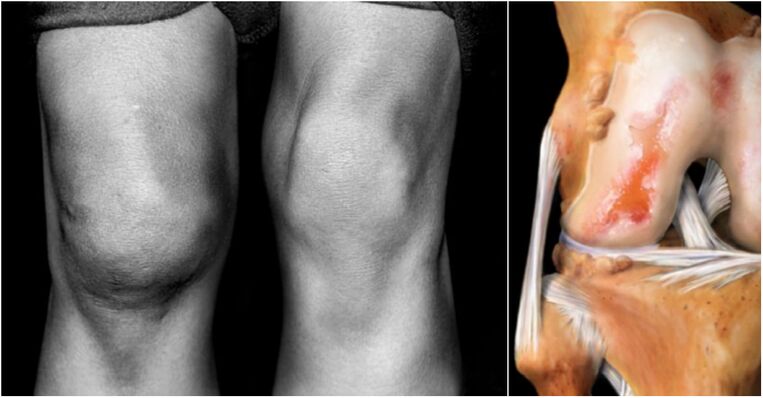
- The summary experiences many changes, increases in size and deformities.You can notice such consequences with the naked eye.
As for acute pain syndrome in the third stage of arthrosis, it appears spontaneously and is practically not located by sedatives available at the pharmacy.In this case, the union prosthetics is the only way out of the situation.
In particularly complex forms of gonartrosis, experts distinguish another phase in which the destruction of the common bag begins.Unfortunately, in modern medicine there are no effective ways to treat the pathology, which has passed in phases 2 and 3. In this regard, doctors recommend timely for the clinic if the slightest suspicion of gonartrosis is detected.
Troubleshooting
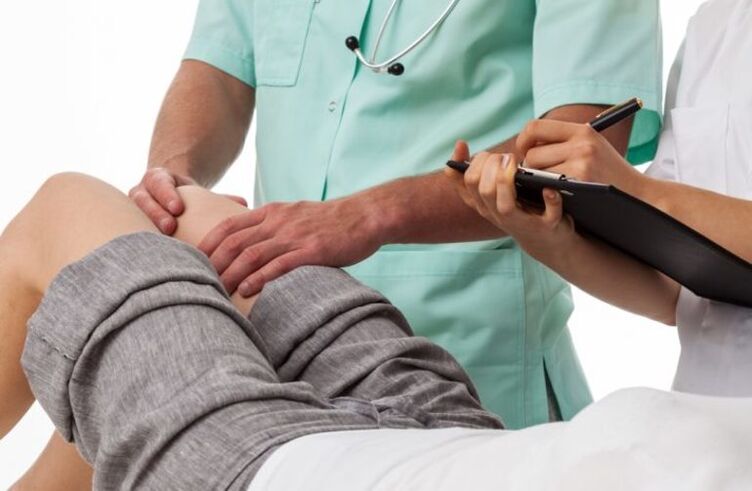
Understanding the causes of gonarthrosis, it is important to know about the correct diagnosis of pathology.After all, you need to be able to distinguish it from other diseases that may have similar symptoms.
To determine the development of the disease, a comprehensive examination is used, which includes a biochemical blood test, radiograph, MRI and ultrasound.It should be noted that with different stages of arthritis, the blood composition remains almost similar, so any change from the norm indicates the presence of another problem.
With regard to this feature, it is possible to make an accurate diagnosis and determine the presence of gonartrosis only with the help of an X -Ray examination.The photo taken clearly shows violations in the structure of the joints and bone, and also determines the surface defects.
However, despite the high accuracy of the diagnosis, X -Ray cannot study soft tissue, including cartilage and meniscus.As an additional product for diagnostics, ultrasound, MRI or CT is used.
If you determine the development of timely pathology and start comprehensive treatment, this will avoid irreparable consequences and prevent the problem from going through more serious stages.However, due to the specific course of the disease, many patients do not even think that joint pain, stiffness and other changes are not the result of fatigue after hard work, but a sign of the onset of degenerative processes.
Treatment methodology
Currently, there are many ways to treat gonarthrosis.They can vary in the principle of action, a list of tasks to be solved, as well as individual characteristics.For a more productive fight against the disease, a comprehensive treatment is used, which is intended:
- Localization of pain.
- Improving mobile functions.
- Improving the condition of cartilage and patient tissue as a whole.
- Strengthen the muscle structure surrounding the affected joint.
The most common methodology for the treatment of arthrosis is physiotherapy.It includes a series of special procedures aimed at strengthening muscle tissue and restoring blood circulation.
During physiotherapeutic treatment, the patient observes a significant improvement in the good -the degenerative processes.However, it is strictly forbidden to start the procedure independently, because the loads calculated unjustly can only aggravate the problem.
By trying to get rid of the pain, relieve swelling and inflammation, it is necessary to use a number of non -steroidal -type medications.These include ibuprofen, Ketoprofen, Diclofenac and others.The task of the drug is to quickly relieve pain for more productive treatment in the future.
If the use of non -steroidal anti -inflammatory drugs does not give any results, you will need to address the use of corticosteroids with a more pronounced anti -inflammatory effect.However, it is not recommended to use the sedative for a long period of time because they only reduce the symptoms, slowing the tissue restoration process.If after receiving a tablet the pain disappeared, it is best to refuse the medication.
External funds and surgical intervention
Causes of common war arthrosis with the help of various ointments, compresses and creams.And although these medicines do not treat arthrosis, they improve the patient's well -being and reduce pain.Among the most effective external remedies, anti -inflammatory heat and voting are distinguished.
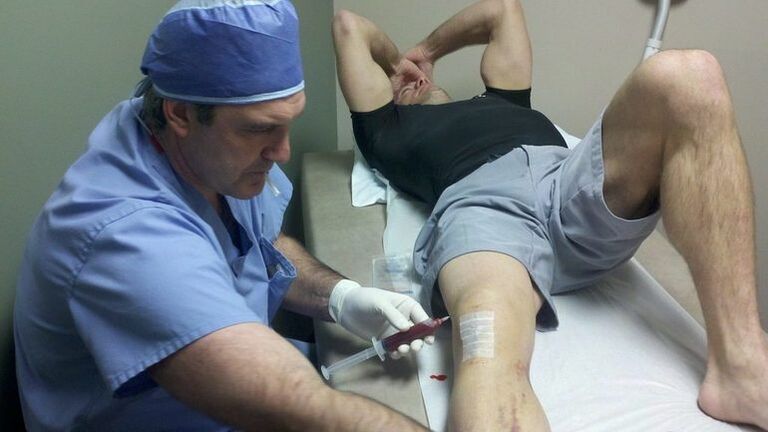
With the development of the second phase of the disease, the patient may prescribe intra -articular injections of corticosteroids, namely:
- Betamethason.
When choosing the medicine, it is necessary to consider his tolerance from the patient.If we talk about corticosteroids, then they are able to effectively eliminate the pain, but not to withstand the severe stages of arthrosis.
If the disease is in the final stage, which is considered more dangerous, surgery will be the only way out.In this case, you will need to surgical decompression of the common bag to expand the lumen between the bones and restore the cartilage surfaces.
Whether this approach is to be effective depends on many factors.First of all, you have to consider the severity of the disease.If it is no longer miserable, it is quite possible to restore the previous joint mobility and get rid of pain.
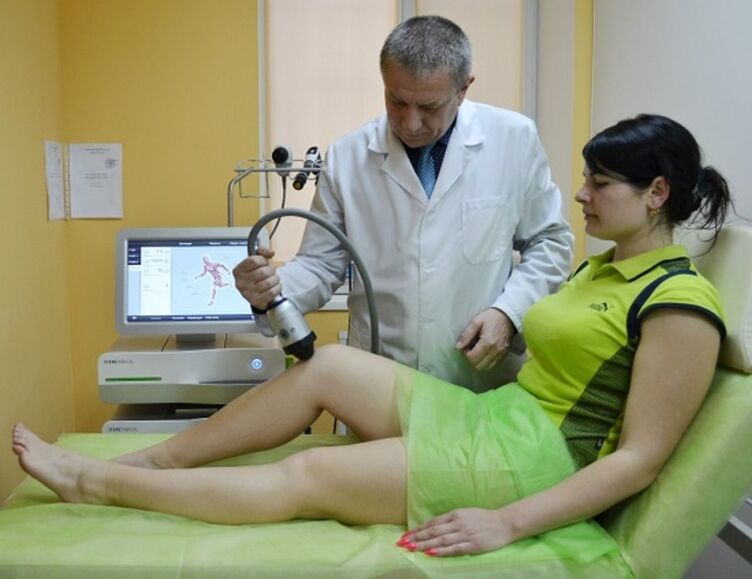
However, the sore knot will still be felt, so the patient should seriously review his life style.It will also be necessary to pay close attention to the exercises of physiotherapy, proper nutrition and proper physical activity.
As a prevention, it is recommended to abandon the consumption of salty or spicy foods, alcoholic beverages and cigarettes.Such actions will positively affect the condition of the body and save the node from unnecessary loads.
Comprehensive treatment of arthrosis in accordance with the above recommendations is the best way to suspend a dangerous pathology and restore the previous functioning of the knee joints.
















































